UK SPONSORSHIP
WHAT IS UK SPONSORSHIP AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT?
All parties involved in the hiring process, the people that are hired fully understand what is involved as
the Home Office can interview you at any time
FIRSTLY, CLICK INTRODUCTIONS, THEN CLICK THE 1-10 IN THEIR ORDER AND FINALLY GO TO AGREEMENT AND ACCEPT YOU AGREE AND FULLY UNDERSTAND WHAT IS REQUIRED
Any party failing to agree to the terms, the visa application will not be processed in accordance to the good HR practices of holding a Home Office sponsor licence
Introducing UK Sponsorship
When employing people in the UK, the UK sponsor being MCB must follow a number of employment guidelines and laws.
We have employment law when engaging paid employees such as religious workers, we then have charity volunteers who are deemed to be volunteers, UK employment and Home Office laws must be adhered to at all times.
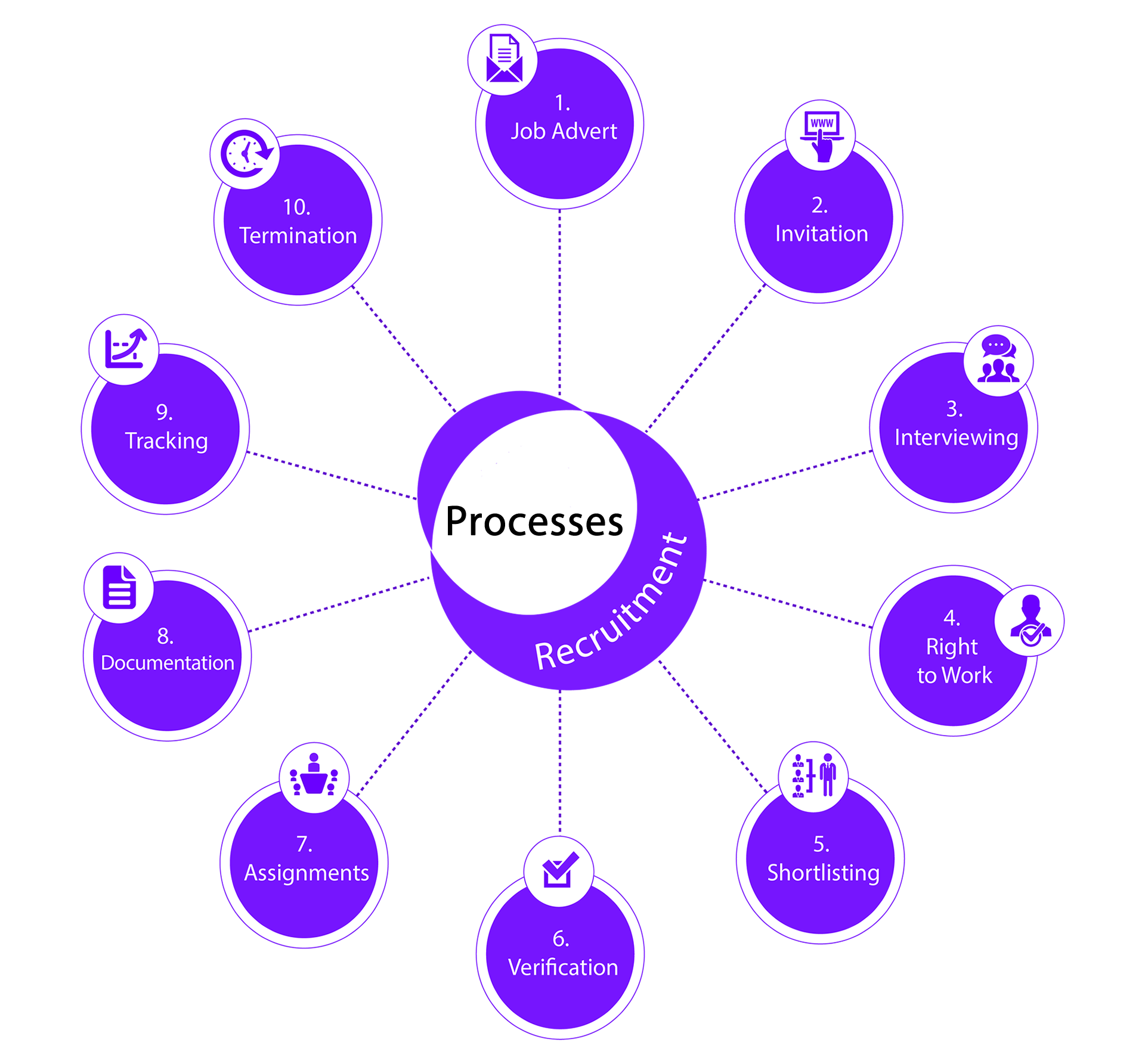
We have put together a 10-step process to help all parties fully understand their obligations on sponsored workers.
BEST PRACTICES FOR WHEN YOU CARRY OUT A RECRUITMENT PROCESS
Did you know employment regulations actually starts from the moment you advertise the job vacancy and not when you offer employment or the person starting the job?
DID YOU ALSO KNOW THE HOME OFFICE CAN LOOK AT ALL 10 PROCESSES AND IF ONE PROCESS IS DEEMED NON-COMPLIANT, MCB CAN HAVE THEIR SPONSOR LICENCE REVOKED WHICH MEANS ALL SPONSORED WORKERS UNDER TIER 2 AND
TIER 5 WOULD ALL LOSE THEIR JOB AND POTENTIALLY BE REMOVED FROM THE UK.
We have illustrated below a 10-step guide to help you understand the steps you may have to take to avoid compliance issues:
If you do not understand the above or need clarification, contact MCB's approved immigration lawyer
10-Step Recruitment Process
1. JOB ADVERTISING
When you post a job, the job advert must comply to the Equality act 2010 guidelines.
Job adverts cannot discriminate any person so be careful when using words such as:
- Age | Race | Sex | Disability | Pregnancy | Maternity | Religion or Belief
When posting a job, the organisation should reframe from using words such as:
- Recent Graduate
| High Experienced*
| Bar Maid
| Handyman
| Advertise to a specific group
*You can use high experienced if the job vacancy was key specific such as highly skilled position. Some business advertise I need a person with x years of experience but this could be classed as discrimination so you need to be careful how you describe a person's skill sets for the job role.
If employing a non-EEA national where a Home Office Resident Labour Market Test (RLMT) is required, this must be advertised in the Jobcentre and another place such as Internet, social media site or newspaper article unless exempt.
2. INVITATION
If the job vacancy needs to comply to the RLMT, the organisation should acknowledge all applicants that apply to the job advertisement regardless if the applicant is suitable or not.
Applicants that seem suitable for the job vacancy, should be informed of this.
When an ‘applicant' or ‘internal member of staff’ applies to the organisation job vacancy, they should follow a certain process to avoid issues which could lead to discrimination and Home Office non-compliance if the job advertisement is related to a Tier 2 or Tier 5 visa application.
Regardless who applies to the organisation's job advert, they should send the applicant a notification (email or SMS) to acknowledge their interest in the job vacancy.
3. INTERVIEWING
When the organisation has decided which applicants they want to interview, some organisations will invite the applicants to their office. Doing this initial process can be very time-consuming, costly in your time and from our research, many people interviewed did not match up to their CVs. Regardless which option you take to do your interviewing, the same process should follow on how you capture and log people's personal information.
Interview Formats:
Online
| Telephone
| Webcam
| Face-to-Face
Online interview is becoming more of a trend as organisations are looking at ways to reduce the hiring costs. The organisation might prefer to carry out a telephone or webcam interview. Some organisation just skip this and invite the applicant in for a face-to-face interview. You must record how the interview went, discussion points, what was promised and action points.
You might be thinking why should I log this?
Did you know, if an applicant felt they were being discriminated against, they can go to ACAS and put in a discrimination complaint against your organisation; you could end up in an employment tribunal.
See Shortlisting section process for Face-to-Face interviewing.
4. RIGHT TO WORK
Before any person can be offered a job, the organisation must carry out a ‘Right to Work’ check first.
If the organisation is thinking of hiring an applicant, they must first verify if that applicant needs permission to work in the UK. If the applicant already holds a UK visa, is it:
- Valid visa and leave still remaining
- Visa permits work with the new organisation without Home Office permission
- If Home Office permission is permitted, can the applicant visa permit UK switching.
- If the applicant is in the UK and cannot switch whilst in the UK or change employers from their Tier to the same Tier for another organisation, they must leave the UK to apply for an entry visa.
TIP
The organisation should never guarantee or promise an applicant a job until a full Right to Work check has been carried out. If the organisation wants to offer a job to an applicant to secure their services but have not yet done a right to work check, they should provide the applicant a ‘Letter of Intent’, add a clause to say, a Right to Work check must be carried out first and only then can we provide you with a formal ‘offer of employment’. This will protect your business.
Right to work falls under various categories, they can include:
Immigration Status
| Licences
| Accreditations
| Insurance.
5. SHORTLISTING
Once the organisation has clarified the right to work status, the applicant can be shortlisted.
Once an applicant is shortlisted, interview notes should be logged and notes added as to why shortlisted.
What is deemed as being shortlisted?
Shortlisting a applicant comes in different flavours, we have:
Not suitable
| Might be suitable
| Very suitable
| 2nd or 3rd interview
When the organisation shortlist an applicant for a job role, it is no different to the initial telephone or webcam interview, the organisation must log what was discussed and promised.
When an applicant attends an interview, ask them to demonstrate their ability to do the role advertised. This could be presenting a PowerPoint to you or, presenting a business plan or, demonstrating at the interview they can do a task like create a web page (IT) or cook a dish (chef) or take a test on areas of manual handling (healthcare professional).
If you are ever challenged over why you selected a person over another, this will help demonstrate you treated each applicant equally.
6. VERIFICATION
When the organisation invites a candidate to a face-to-face interview, ask the applicant to bring in their original right to work evidence to the interview. Right to work evidence will depend on their job role but certain documents must be provided such as travel ID or similar document.
Some interviews are done in one or multiple stages, this all depends on the type of role.
Tip
When the organisation take copies of right to work evidence, they must do the following:
- Write the applicant's full name as shown in the travel ID
- Add the days date
- Add the organisation person job title
- Sign the photocopy and state you have seen the original.
Now file the evidence whether as a hard copy or as an electronic file.
7. CONTRACT
Prior to offering the applicant an offer of employment, has the organisation done the following checks:
- Compiled a list of every applicant that applied to the job vacancy?
- Logged all CVs, covering letters and applicants' other evidence?
- Added notes of who was shortlisted and not shortlisted?
Added interview notes for all applicants spoken to who applied to the job.
Only offer a 'Contract of Service' (employment) if the applicant can work for your organisation.
The employment law states employees are titled to a number of documents which could include from this list: Statement of main terms of employment (Permanent or Temporary) | Employee Handbook Form for Existing Employees | Restrictive Covenant | Deductions from Pay | 48 Hour Opt Out | Action Plan Form | Action Plan Letter Form | Action Plan Monitoring Form | Job Task Performance Table Form | Notes and forms for appraisers | Notes and forms for employees | Preparation for Appraisal Form | Performance Appraisal Form | Change of Personal Details | Staff Appraisal Scheme | Customer Complaint Form | Disciplinary Record – Form | Display Screen Equipment Form | Employee HS Induction Training Record | Equal Opportunity Monitoring Form | Exit interview | Flexi-time Request Form | Health Questionnaire Holding Letter | Holiday Request Form (Hours) | Holiday Request Form (Days) | Holiday Request Form (Shifts) | Interview Rating Form | Person Specification Preparation Form | Personal Details Form | Pool Vehicle Log Form | Reference Letter | Rejection Letter | Return to work interview Form | Job Descriptions | Short Listing Form.
8. DOCUMENTATION
It is essential that any documents the organisation has on an employee is filed correctly. Documents that should be filed include:
- CV
- References
- Qualifications
- Immigration status
- Licences
- Accreditations
- Interview notes
- Other evidence to demonstrate ability to do the job.
- Employment related documents that are listed above under section Contract.
An employee has the right to know what documents/data the organisation holds on them. Data is normally stored manually or electronically. Employees’ personal data should be kept safe, secure and up to date by the organisation at all times. Below is the type of data the employer should keep about their employees:
- Name
- Address
- Date of birth
- Gender
- Education
- Qualifications
- Work experience
- National Insurance Number
- Tax Code
- Details of any known disability
- Emergency contact details
Other details that should be kept include:
- Employment history with the organisation
- Employment terms and conditions (e.g. pay, hours of work, holidays, benefits, absence)
- Any accidents connected with work
- Any training taken
- Any disciplinary action.
What the organisation should tell their employee and their rights:
- What records are kept and how they’re used
- The confidentiality of the records
- How these records can help with their training and development at work
- If an employee asks to find out what data is kept on them; the organisation will have 40 days to provide a copy of the information.
9. TRACKING
It is essential the organisation tracks all essential data/documents held on an employee. Depending on the employee, if under immigration control, the following could be filed and where documents have expiry dates, these are tracked. Types of documents include:
- Travel IDs
- Visa (Biometric Resident Permit unless non-EEA national has other Home Office approval status)
- UKVI CoSs
- DBS Licence
- ACS Licence
- BBA Licence
- CITB Licences
- CAA Licence
- CSCS Cards
- CSR Cards
- DVLA Licensing
- ECS Cards
- EUSR Cards
- GMC Licence
- GSR Licensing
- Health & Safety
- JJB Cards
- IPAL PAL Cards
- LANTRA Cards
- NMC pin
- Mandatory Training
- MPQC Cards
- SCORE Cards
- Sentinel Cards
- SIA Badge to name a few.
Basically, any legal document required to say the worker is permitted to do that work, must be logged and tracked.
10. TERMINATION
When a member of staff leaves their employment, employees are either:
- Dismissed
- Resigned
- Made redundant
- Retired
Dismissing Staff
Dismissal is when you end an employee’s contract. When dismissing staff, you must do it fairly and log all information. If the UK organisation dismissed a Tier 2 or Tier 5 worker, they have 10 working days to login to their SMS and report it to the Home Office.
There are several types of dismissal:
- Fair dismissal
- Unfair dismissal
- Constructive dismissal
- Wrongful dismissal.
Resigned
A UK organisation cannot refuse to accept an employee's resignation. They must follow certain procedures. When an employee resigns the UK organisation must:
- get them to confirm their resignation in writing
- tell them what their notice period is
- agree when their last day at work will be
- confirm whether they should work all or part of their notice period
- Update the UK organisation SMS within 10 working days if the worker is on a Tier 2 or Tier 5 CoS.
Note: An employee's decision to retire is a form of resignation.
Important Message
Verbal resignations given in the heat of the moment could lead to claims of unfair dismissal - always ask for resignations to be given in writing.
Redundancy
Redundancy is when the UK organisation dismisses an employee because they no longer need anyone to do their job. This might be because the business is:
- changing what it does | doing things in a different way, for example using new machinery
- changing location or closing down
Important Notice
For a redundancy to be genuine, the UK organisation must demonstrate that the employee’s job will no longer exist.
Redundancies can be compulsory or non-compulsory. If the UK organisation do have to make redundancies, they can get help from Jobcentre Plus.
Employee rights - Employees have certain rights and may be entitled to redundancy pay if they’re made redundant.
TIP
Regardless how the employee leaves their job, log as much information as possible. Information should be how they left their employment, hand over been correctly done, left on good note, reasons for leaving, log performance for future references and finally, log if any holiday pay and other benefits should be paid to the employee.
Staying Compliant
If you require us to first validate your organisation, you can request a free 30 minute consultation.
Before we accept your UK organisation, we will send you a questionnaire form to complete so we can ascertain how you operate your recruitment cycle.
Information provided by you is strictly confidential and will only be used for the purpose of evaluating your organisation
Once we know your organisation strengths and weaknesses, we will explain how we can help you.